Back-to-back testing in OSS/BSS
Julia Liber is head of Telecom and Web application testing department at a1qa . In this role, she manages the Internet applications and telecom systems testing team and provides consulting for wireless operators. She also assists with organizing the testing process and the acceptance phase for modification or new billing solution implementations.
Would you say testing in OSS/BSS is a trivial task? Definitely not
It usually takes at least a couple of days just to test functionality. While implementing a new system/subsystem or changing functionality, there are so many questions to be answered. Which product to choose for testing? Which tariff plan to choose for testing? What kind of charges to check, and what type of subscribers to use?
It is obviously impossible to cover all possible options and combinations during functional testing, so it is necessary to select the most important products and services.
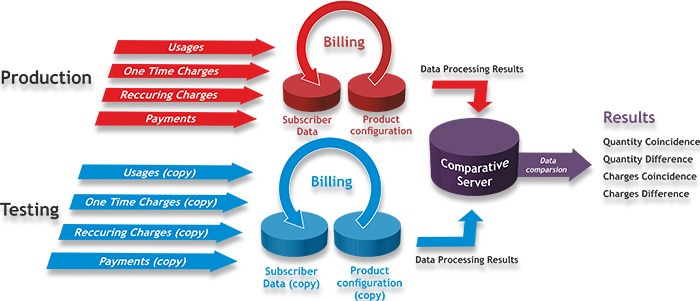
At this point, the thought comes to mind to turn to the good old engineering approach of back-to-back testing, which is based on the law of large numbers. The point is simple: It is necessary to compare system behavior using the same data. Imagine that we have two environments:
- Production — your live system serving subscribers
- Testing — your environment intended for testing.
First, at a specific date/time, usually after a billing period has been completed, we transfer copies of user data (migration data) and the product catalog (configuration data) to the testing stand. At the end of the reporting period (month or week, depending on the timing of the invoice), a copy of the input data for each transaction (payments, charges, maintenance fees) is loaded into the testing environment.
First, the output data has being processed from both environments. Second, it is placed on a comparison server. Then, specially developed script checks if the number of transactions and the charges from both environments match. The matching and unmatched numbers, the results of this comparison, are the input data for testers.
What’s next? The testing team goes to work. Testers analyze the records based on any discrepancies between the two sets of results. The causes for the differences are identified, the records are grouped into causes, and we get the results in the following format:
Numerical discrepancies:
- 5 percent of records could not boot due to a functional defect 1
- 3.5 percent of records could not be loaded due to a functional defect 2
- 1 percent of records could not boot due to a functional defect 3
- 0.5 percent of records could not be loaded due to a functional defect 4
Discrepancies in the amount of write-offs:
- 7 percent of records are processed improperly because of a defect in the configuration No. 5
- 1 percent of records are processed improperly because of a defect in the configuration No. 5
- 0.5 percent of records processed improperly because of a defect in the configuration No. 5
- 0.1 percent of records processed improperly because of a defect in the configuration No. 5
What is the outcome of this approach?
- It provides complete coverage of the product catalog, through the activities of real users. The system tests exactly what is used by subscribers;
- It checks the quality of the configuration and system migration, as well as the most critical functionality for OSS/BSS parts: rating, billing and payments;
- It helps clearly prioritize defects that are present in the system based on the needs of the business. Let’s say, it is more important to correct defect No. 1, compared to defects No. 3 or No. 4, since defect No. 1 does more damage to the business;
- Because testing takes place on a large volume of data, this is a good way to test how well the new version of the system can withstand real-world loading.
Of course, there are limitations to this approach.
First, the data comparison is always dependent on what type of OSS/BSS you use. It will be necessary to develop a unique script for your system to compare and select data to analyze. Second, in the ideal case, the test environment must comply with the product environment. Otherwise, there is a risk that you won’t meet the deadline because the test environment processes transactions too slowly.