Fortifying retail security posture: embracing zero trust to protect customer data
In 2023, we witnessed a 20% surge in data breaches in the retail industry across the US, highlighting the critical need for robust security measures to safeguard customer data. From Amazon and Home Depot to eBay and Under Armour, the fallout from these threats included eroded customer trust, financial losses, and damaged reputation.
In today’s high-risk landscape, implementing traditional security models isn’t enough to tackle sophisticated cyber incidents. The concept of zero trust (ZT) emerges as a beacon of resilience, offering businesses a proactive approach to fortify their overall safety posture and protect sensitive end-user information.
In this article, we’ll delve into core reasons why retailers should leverage ZT as well as learn hands-on recommendations to enhance resistance to internal and external cyberattacks.
A zero trust concept in retail: 5 reasons to adopt
According to the State of Zero Trust Security by Okta, 97% of surveyed C-level executives, operating in financial, healthcare, government, and other sectors, implemented a ZT security initiative in 2022.
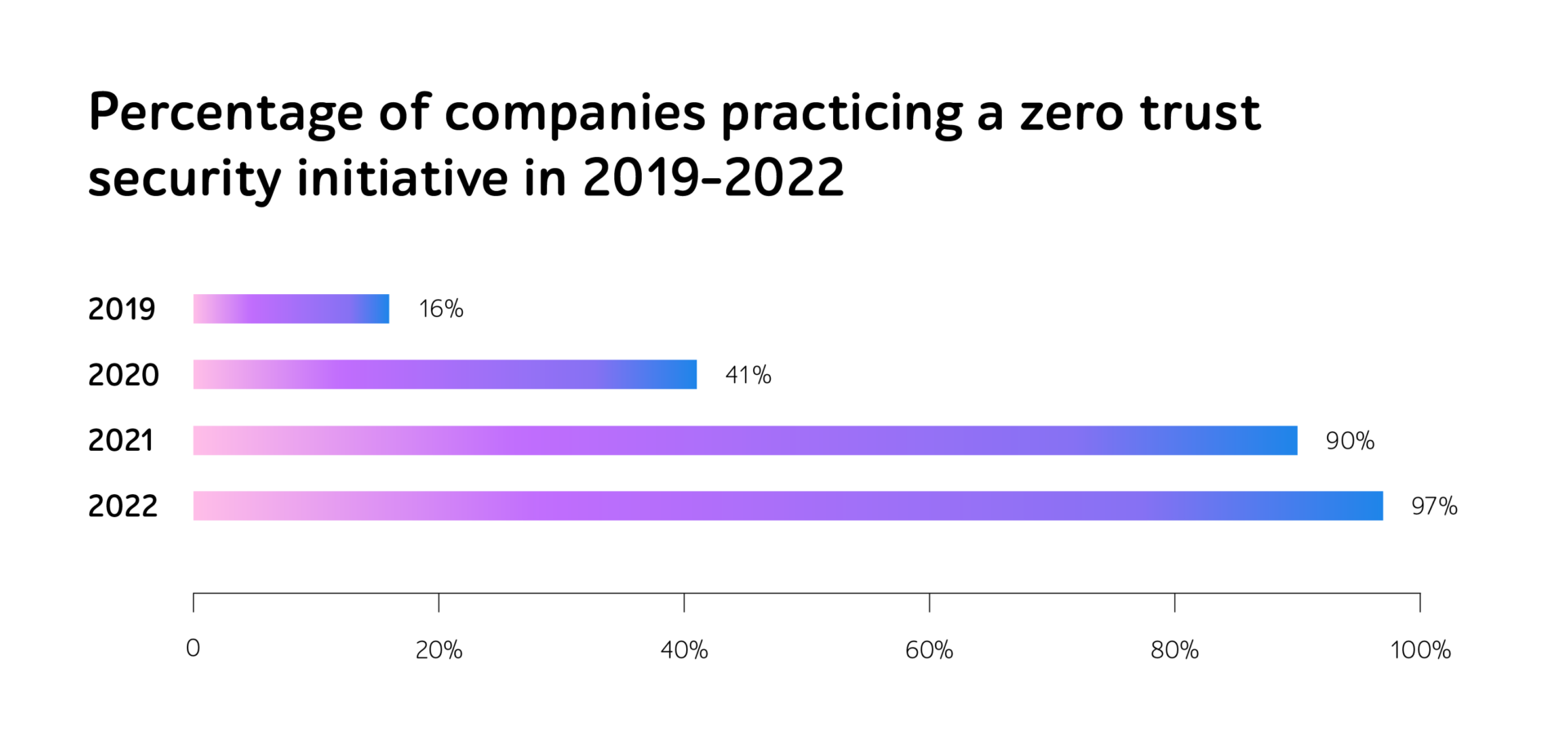
Source: State of Zero Trust Security 2022
Zero trust instills a fundamental shift in mindset, treating every user, device, and network segment as a potential threat until proven otherwise. Its principles include explicit verification to validate based on all available data points, usage of least-privilege access to decrease the risk of unauthorized data exposure, and breach assumption to enhance threat detection and improve defenses.
This approach advocates for strict access controls, continuous authentication, and micro-segmentation to minimize the attack surface and mitigate potential hazards. And it is particularly critical in the retail sector, where the storage of personal and financial clients’ data in different places, including the cloud, can be vulnerable to attacks.
Retail environments often feature complex interconnected systems, ranging from ERP and CRMs to POS systems in physical stores. This interconnectivity increases the susceptibility to threats, such as malicious software infiltrating the POS systems or phishing attacks targeting employees to gain access to sensitive information.
Here are the reasons why retailers should introduce zero trust:
- Enhanced security posture. A ZT concept helps companies ensure that all attempts to penetrate the system are rigorously verified while mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches, such as a hacker attempting to exploit vulnerabilities through the shop’s Wi-Fi network.
- Strengthened resilience. By implementing micro-segmentation and enforcing strict access controls, zero trust ensures that customer sensitive information or financial data are isolated from each other, limiting the scope of potential attacks. This helps reduce the overall impact and cost of recovery as well as time to breach detection.
- Increased end-user confidence. By safeguarding clients’ sensitive information and preventing leakages, retail businesses uphold their commitment to data privacy and maintain consumer trust, fostering long-term brand loyalty and reputation.
- Improved adaptability to dynamic environments. In the era of cloud computing and remote work, ZT allows organizations to safeguard data and resources regardless of the location, network boundary, or device type used in retail, like self-checkouts and cash desks.
- Intensified control. Zero trust architectures provide retailers with greater visibility and control over their network traffic and user activity. Through continuous monitoring, they can gain insights into user behaviors, identify anomalous activities, and respond to security incidents in real-time.
- Future-proof against emerging threats. By regularly updating and refining safety controls and policies, companies stay ahead of cyber adversaries and timely mitigate the risks posed by new attack vectors and exploitation techniques.
5 tips to ensure robust cyber defense for retail businesses
To fortify defenses against evolving digital threats and safeguard retail operations, we suggest embracing a holistic cybersecurity strategy designed in line with zero trust principles and QA best practices.
Tip #1. Conduct risk assessment
These checks help identify potential system vulnerabilities. By evaluating the possible risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access early on, retailers can develop targeted security controls and measures to mitigate weaknesses effectively.
Tip #2. Implement stringent access controls and security policies
Retail companies should prioritize incorporating access controls as part of their cybersecurity strategy. By implementing access controls based on user roles, responsibilities, and business needs, they enhance security while maintaining operational efficiency.
Thus, they ensure that only authorized individuals or roles have the necessary permissions. Moreover, with QA at the core, they confirm that access controls are properly configured and consistently enforced across the network, reducing the risk of potential data breaches.
Additionally, introducing robust security policies that govern the frequency of security actions and prioritize staff education about safety measures is crucial for maintaining a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
Tip #3. Adopt test automation for security activities
To optimize security operations and improve overall efficiency, retailers can leverage test automation. By incorporating automated security tests into their workflows, businesses can efficiently scan systems, evaluate permission levels, and identify users with granted permissions. These tests provide detailed reports highlighting any mismatches or potential vulnerabilities, empowering organizations to address issues promptly.
Thus, they streamline routine tasks, including threat detection, incident response, and compliance monitoring while freeing up valuable time and resources for core activities.
Tip #4. Develop a comprehensive incident response plan
It’s mission-critical to meticulously outline procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity incidents in line with zero trust principles. The plan should also include a list of possible risks, probability of their appearance, and actions to prevent them or mitigate their outcomes.
By defining clear roles and responsibilities for incident response team members and establishing robust communication channels for reporting and escalating incidents, businesses ensure coordinated reactions to security breaches.
Tip #5. Provide safety awareness training for employees
Organizations can empower their workforce to recognize and respond to potential safety risks. For that, they should educate all specialists — administrators, business representatives, store managers, and consultants — about the principles of ZT, the overall company security measures, common cyber threats, and best practices for data protection.
Regular security awareness training sessions foster a culture of vigilance across the organization. To evaluate the effectiveness of training programs and enhance their employees’ readiness to combat digital incidents, organizations can introduce social engineering practices, like simulated phishing exercises, baiting, business email compromise, and quid pro quo.
In a nutshell
The imperative for retail businesses to fortify their cybersecurity defenses has never been more urgent. The interconnected nature of digital operations coupled with the growing sophistication of cyber threats requires a comprehensive approach to security.
For that, companies can conduct risk assessment, implement stringent access controls and security policies, adopt test automation for security activities, develop a comprehensive incident response plan, and promote safety awareness training for employees.
Planning to enhance the security level of your software products? Get hold of a1qa’s team and obtain professional support.